
Undergraduate
Researcher Bin Wang and Associate Professor Xiaoxia Lu led a team to win the interdisciplinary Third prize at the 32st "Challenge Cup" held by Peking University
The results of the 32nd "Challenge Cup" series of events at Peking University have been announced recently. In this year's competition, students Yang Shuo and Wang Lingzhang from the School of Public Health, and Yi Xiaolong from the College of Urban and Environmental Sciences, leveraged the strengths of their respective disciplines. Under the guidance of Professor Wang Bin (School of Public Health) and Professor Lu Xiaoxia (College of Urban and Environmental Sciences), they completed the project "Constructing a Big Data Database on Environmental Health and Machine Learning Models to Predict the Epidemiological Health Risk Effects of Chemicals," achieving third prize in the interdisciplinary category.
Project Introduction
With the rapid increase in the variety of chemicals, assessing the health risks these substances pose to populations has become a significant challenge. Due to their vast numbers and the lack of toxicological data, especially the difficulty and cost of obtaining their health risk effect values (such as Relative Risk (RR) and Odds Ratio (OR)), the health risk assessment of a large number of chemicals has been severely delayed.
This study first selected a series of typical environmental chemicals and diseases based on big data retrieval and literature summarization, integrating published meta-analysis studies to construct a database of epidemiological health risk effect values. Then, RDKit was used to obtain the molecular structure similarity of the chemicals, and public toxicological databases such as CTD (Comparative Toxicogenomics Database), T3DB (Toxin and Toxin Target Database), and ToxCast (Toxicity Forecaster) were integrated to obtain biological action similarity information. Through feature selection, 11 high-contributing variables were retained for modeling analysis. Finally, different machine learning algorithms were used to construct quantitative and classification models to predict the health risk effect values and risk categories of chemicals.
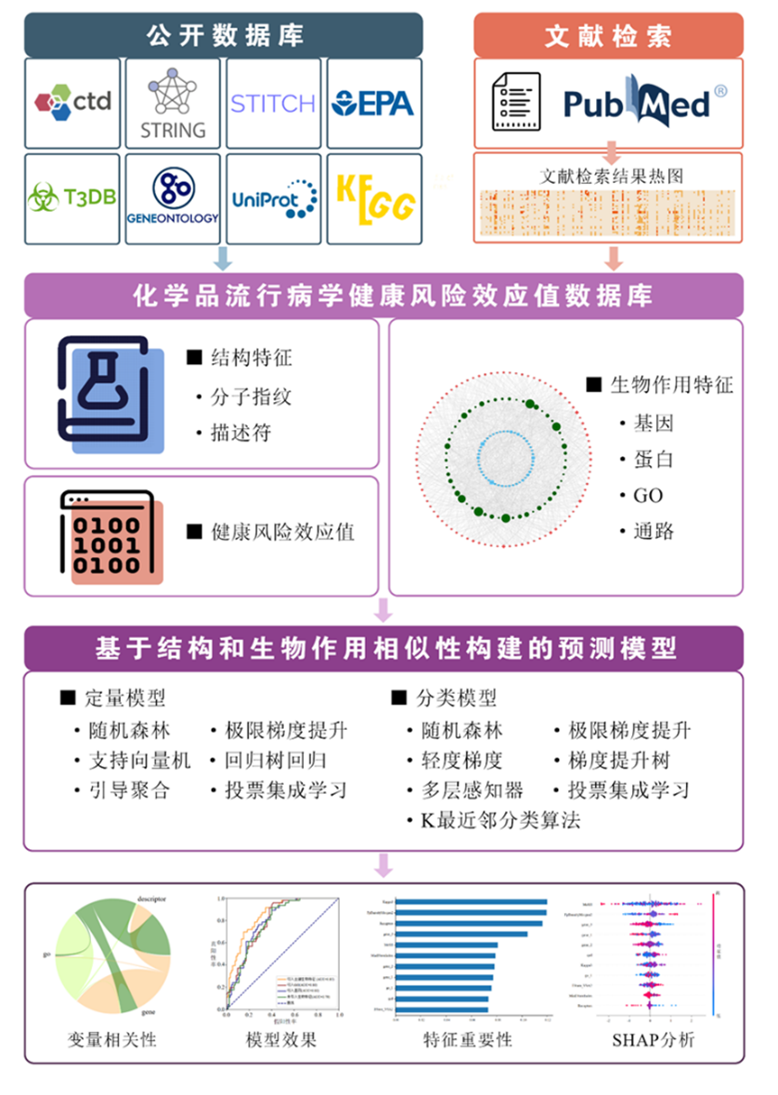
Figure 1. Overall Study Design
Award Acceptance Speech
Environmental exposomics has been a research hotspot in environmental science in recent years, while public health focuses on exploring issues related to human diseases and health from a population perspective. This study combines the topic of environmental health, which has significant scientific importance, leveraging the interdisciplinary integration of environmental science and public health to explore the possibility of predicting the health risk effect values of chemicals based on their similarities.
During the project, students from the College of Urban and Environmental Sciences were responsible for integrating databases related to environmental exposure and multi-omics information, providing unique insights into handling high-dimensional exposome data. Students from the School of Public Health utilized their knowledge of epidemiology and health statistics to construct multi-omics networks and risk prediction models. The three team members worked closely together, effectively dividing tasks and collaboratively exploring scientific issues related to the impact of environmental exposure on health from a population perspective. The two professors provided substantial support during the research process. Professor Wang Bin offered significant assistance in research theory, project design, and technical guidance, while Professor Lu Xiaoxia meticulously guided the research ideas, supervised and checked the research progress, and provided writing suggestions. All team members gained a lot from this project, acquiring many new skills, from database organization to data analysis, and from drawing to text writing. "The road ahead is long and arduous; I will search high and low," expressing hope that we will remain true to our original aspirations on our future research path.
Team Members
Student Profiles

School of Public Health
Shuo Yang
Undergraduate Student in Preventive Medicine, Class of 2020

School of Public Health
Lingzhang Wang
Undergraduate Student in Preventive Medicine, Class of 2021

College of Urban and Environmental Sciences
Xiaolong Yi
Undergraduate Student in Environmental Health, Class of 2021
Faculty Profiles

School of Public Health
Bin Wang, Researcher
Research Direction: Environment Health, Exposome, Bioinformatics and Artificial intelligence

College of Urban and Environmental Sciences
Xiaoxia Lu, Associate Professor
Research Direction: Environmental behavior and health effects of emerging pollutants, remediation of polluted environments
Contributed by | Professor Bin Wang's Team (Peking University)
Reviewed by | Bin Wang

